Trend Reports
India Country Report: Growth, Policy, and Market Trends

Summary
India’s 4Q24 growth slows to 6.2% amid industrial drag, but rising consumption, digital innovation, and reform-driven policies provide optimism.
India’s 4Q24 Growth Slows Despite Easing Inflation
India’s GDP expanded by 6.2% year-on-year in Q4 2024, falling short of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) target of 7.4%. Although this marked an uptick from Q3’s 5.6%, it was a clear slowdown compared to 9.5% growth in Q4 2023.
GDP 1Q24-4Q25 | 4Q24 GDP Growth Improves but Stays Below ~7% Target
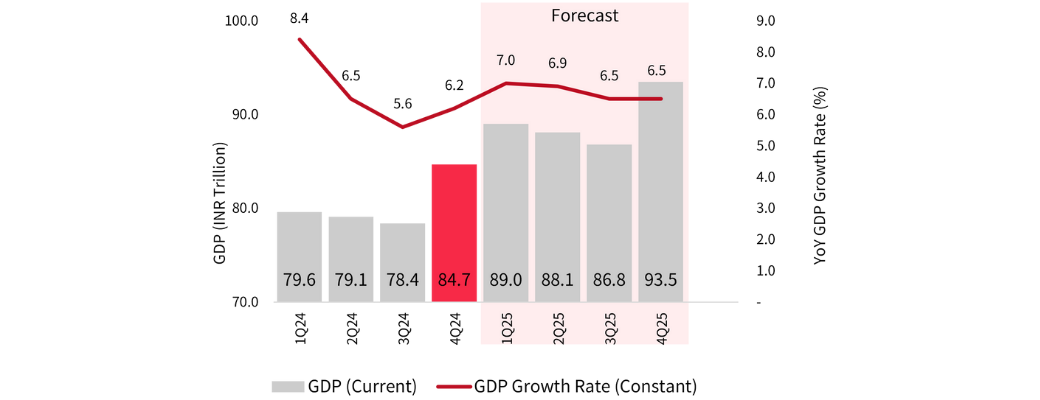
Industrial performance remained subdued, limiting the overall growth momentum despite steady gains in services and a mild recovery in agriculture.
On a nominal basis, India’s GDP stood at INR 84.7 trillion (USD 987.3 billion).
Key growth drivers included:
- Private consumption (+6.9% YoY)
- Government spending (+8.3% YoY)
- Exports (+10.4%), with imports declining on a weaker rupee
To support growth, the RBI cut the repo rate by 25 basis points in February 2025—its first cut since early 2023. This came as retail inflation eased from 6.2% in October to 5.2% in December 2024, with projections pointing to an average of 4.4% in Q1 2025.
Lower inflation and cheaper credit are expected to boost domestic demand, particularly in consumer-driven sectors.
Political Stability Returns with Reform Push
India’s political landscape in Q4 2024 was defined by a key democratic milestone and a pro-growth fiscal strategy, signalling renewed efforts to strengthen governance and economic resilience.
In a historic development, Jammu and Kashmir held its first assembly elections since the abrogation of Article 370 in 2019. The elections, conducted in three phases with 63.9% voter turnout, marked the return of local governance after years of President’s rule. The National Conference–Congress alliance won a majority with 42 seats, paving the way for Omar Abdullah to assume leadership.
This political transition is expected to support peace, regional stability, and the economic integration of an area rich in mineral and solar energy resources.
In parallel, the Union Budget for FY2025–26 outlined several key measures to boost domestic demand and entrepreneurship, including:
- Tax-free income threshold raised from INR 700,000 to INR 1.2 million
- INR 1 trillion fund of funds launched to support start-up financing
- MSME credit guarantees doubled, enhancing access to capital
- R&D tax incentives expanded, with increased funding for the India AI Mission
Together, these developments reflect a dual push for political stability and economic activation, reinforcing investor confidence in India’s macroeconomic trajectory.
Source: Tribune India | BBC | Reuters | APN News | CAG | Kashmirobserver
Consumption and Digital Adoption Drive Social Shifts
India’s population reached 1.46 billion in Q4 2024, with over one-third aged 20–39, offering a strong demographic advantage. However, the employment rate declined slightly, highlighting structural challenges. White-collar hiring rose 10% year-on-year, especially in oil & gas, pharma, and IT, while female workforce participation and formal employment both improved.
Rising Discretionary Spending and Changing Consumer Habits
Households spent 29% of income on non-essential goods, led by fashion and electronics. The festive season saw strong demand for fast fashion and sustainable celebrations. Meanwhile, 33% of income went to debt repayments, with the remainder covering essential expenses.
Digital Transactions Reach New Highs
India’s digital economy continued expanding, with UPI processing 16.7 billion transactions in December 2024—an 8% monthly increase—driven by growing person-to-merchant use and broader financial inclusion efforts.
Source: Population Foundation of India | Businessworld | Entrepreneur | PwC
Technological Advancements Reinforce Innovation Path
India’s technological landscape in 4Q24 advanced significantly, driven by investment in artificial intelligence (AI), cloud infrastructure, and semiconductor manufacturing. Major firms and government institutions deepened their focus on digital transformation, reinforcing India’s aspirations to become a global technology hub. Infosys, for instance, launched AI-powered platforms to enhance customer experiences, leveraging partnerships such as that with LivePerson to implement conversational AI. This aligns with the broader push across Indian corporates to integrate generative AI into customer engagement and enterprise operations.
In the healthcare sector, AIIMS and Wipro GE Healthcare announced the launch of the “AI Health Innovations Hub”, a strategic partnership focused on AI applications in cardiology, oncology, and neurology. Wipro GE committed approximately USD 1 million over five years, highlighting the growing convergence of healthcare and digital technology.
Meanwhile, Tata Electronics partnered with Taiwan’s PSMC to establish a semiconductor fabrication facility valued at INR 915 billion. This development underscores India’s ambition to localise high-tech manufacturing and reduce import dependence in critical sectors such as electronics. Government incentives through the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme and semiconductor-focused policies in states like Uttar Pradesh have further bolstered this momentum.
Source: Ministry of Communications | Ministry of Electronics and IT | Niramai | Quectel | Infosys
ESG Underperformance and Rising Environmental Compliance
ESG Underperformance and Rising Environmental Compliance
India’s environmental landscape was shaped by a mix of market underperformance in ESG-linked assets and tightening environmental regulations. While the broader NIFTY Total Market Index declined by 7.5% during the quarter, the NIFTY 100 ESG Index and the NIFTY 100 ESG Sector Leaders Index fell even more sharply—by 8.6% and 9.7% respectively. This trend reflects growing investor caution, influenced by global economic uncertainty and limited near-term returns from ESG-compliant companies, despite long-term sustainability goals.
At the same time, India moved ahead with environmental policy reform:
- From April 2025, new rules will regulate the recycling and disposal of end-of-life vehicles, aiming to minimise environmental harm and encourage responsible scrappage.
- From July 2025, all plastic packaging must include barcodes or QR codes with product and recycling details—enhancing traceability, producer responsibility, and supply chain transparency.
These developments signal a clear shift toward more enforceable ESG standards, with implications for both corporate compliance and investor strategy.
Source: NSE Indices | NIFTY 100 ESG Sector| India Law| Corp Seed
Legal Reforms Aim to Boost Start-ups and Simplify Taxation
India’s legal and regulatory environment in 4Q24 saw targeted reforms aimed at bolstering entrepreneurship, encouraging foreign participation, and simplifying compliance. The Union Budget introduced several measures to improve the ease of doing business, particularly for start-ups and MSMEs.
A notable highlight was the creation of an INR 1 trillion fund of funds for start-ups, designed to provide access to long-term capital and reduce financing constraints. Additionally, credit guarantee schemes for MSMEs were expanded to INR 1 trillion, while research and development activities received enhanced tax incentives.
Source: PWC | PWC Tax Summaries| clear tax |TOI
Outlook Remains Positive Despite Near-Term Headwinds
India ended 4Q24 with mixed signals—moderating GDP growth offset by stable inflation, easing interest rates, and proactive policy measures. The Reserve Bank of India projects full-year GDP growth of 6.4%, slightly below earlier forecasts but still among the highest globally. Falling borrowing costs and fiscal support are expected to aid industrial recovery and capital formation in early 2025.
Government priorities such as infrastructure investment, tax relief, and digitalisation are likely to bolster private consumption and attract investment, particularly in high-growth sectors like semiconductors, AI, and healthcare. Structural shifts—such as the rise of Global Capability Centres, wider UPI adoption, and improved female labour participation—further support the medium-term outlook.
Nonetheless, risks such as uneven employment growth, high household debt, and underperforming ESG assets may weigh on progress. Still, regulatory improvements and long-term reforms offer a foundation for stronger, more inclusive growth. Entering 2025, India remains well-positioned to maintain its status as a global growth leader.
Explore ASEAN Business Insights
Whether you’re tracking GDP trends, policy shifts, or sector performance, Speeda equips you with data-rich, analyst-written reports to drive strategic decision-making.
Unlock Speeda’s full suite of ASEAN country reports, industry research, and Asian company data with a free trial. Sign up to get instant access to in-depth macroeconomic insights like this India 4Q24 Report—plus exclusive coverage across ASEAN markets.


















