Trend Reports
ESG Analysis of Malaysia’s Oil and Gas Sector

Malaysia’s O&G Sector: Key to Sustainable Economic Future
| How Global ESG Pressures Are Forcing a Strategic Shift in Malaysia’s Energy Sector
Malaysia’s oil and gas (O&G) sector is a cornerstone of the nation’s economy, contributing approximately 20% to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and accounting for about 75% of national energy consumption. This significant economic reliance places immense pressure on the sector to align with evolving global Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards. The ambition is not merely compliance, but to emerge as a regional ESG leader and a preferred destination for ESG-conscious investors.
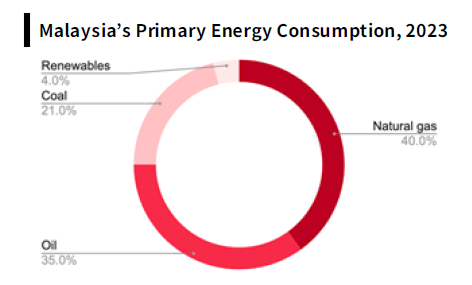
Source: US Energy Information Administration
Despite Malaysia’s contribution of less than 1% to global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions , the nation was ranked 30th globally for total GHG emissions in 2023 , highlighting persistent challenges in achieving its emission reduction targets. The country’s energy mix in 2023 remained heavily reliant on fossil fuels, with natural gas (40%) and oil (35%) dominating, while renewables constituted only 4%. This dependency on traditional energy sources continues to attract scrutiny, particularly concerning high emissions and ongoing investments in new O&G projects.
| ESG Progress: Moderate Gains, Major Gaps
The industry’s current ESG score of 5.8 indicates moderate progress. This score reflects a continuous struggle to effectively balance sustainability objectives with economic interests. While Malaysia has implemented measures such as mandatory sustainability reporting and investments in renewable energy, issues like greenwashing and inconsistent implementation continue to impede its ESG advancements. This underscores the critical need for more robust commitments and improved execution to bridge the gap between policy ambitions and tangible outcomes.
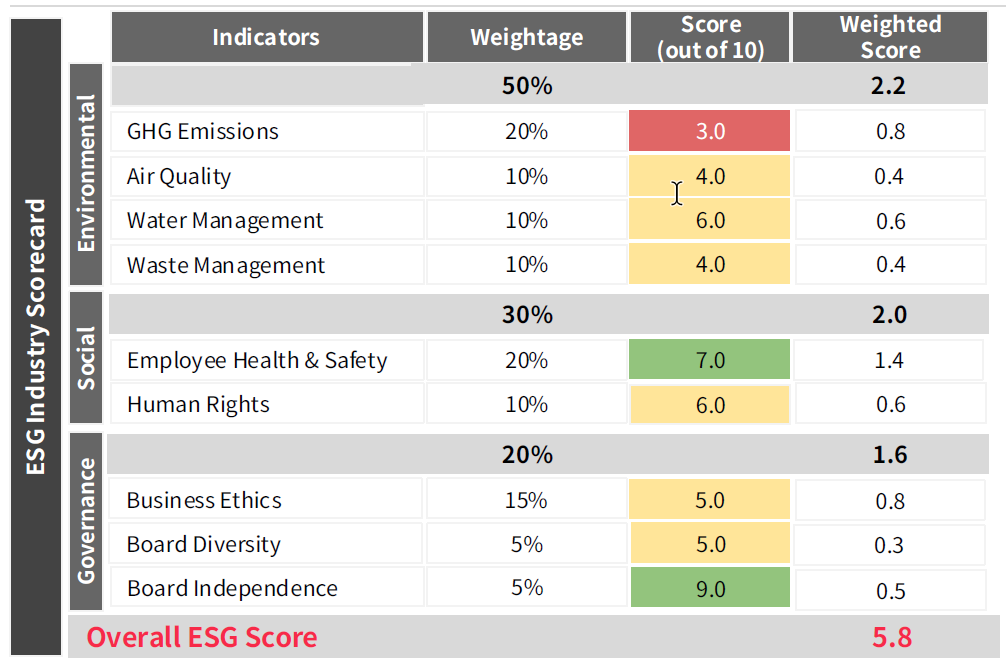
Environmental Gaps Persist Despite Green Efforts
| Striving for Decarbonisation Amid Persistent Carbon Challenges
Environmental performance remains a significant challenge for Malaysia’s O&G sector, particularly concerning greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, water management, and waste disposal. Although GHG emissions from fuel exploitation declined from 18% in 2000 to 13% in 2023 , the slow adoption of low-carbon strategies and an increasing reliance on coal present substantial hurdles to achieving the national net-zero target. Malaysia’s National Energy Transition Roadmap (NETR) sets ambitious goals: net-zero emissions by 2050 and a 32% reduction in energy sector emissions by 2030 (compared to a 2019 baseline). Government initiatives, including the Voluntary Carbon Market and a proposed Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS) bill, underscore this commitment. Leading companies like PETRONAS have allocated substantial capital expenditure towards decarbonisation, targeting significant reductions in Scope 1 and 2 emissions, and actively investing in large-scale CCUS projects such as Kasawari Gas. While PETRONAS shows strong efforts in emission reduction, other companies like Dialog and Hengyuan Refining have made less progress.
| Water and Waste Management: Progress, but Risks Remain
Water management is increasingly critical due to declining reserves, stricter environmental regulations, and pollution concerns, exacerbated by expanding deepwater exploration. Policies like the National Water Resources Policy and the Zero Discharge Policy aim to promote sustainable water management. Companies such as PETRONAS, through initiatives like Project Air Mentah RAPID (PAMER) and the PIC Raw Water Treatment Plant, focus on preventing waste and securing supply.
Proper management and disposal of scheduled waste are crucial for regulatory compliance, environmental protection, and workforce safety. Malaysia’s Environmental Quality (Scheduled Wastes) Regulations 2005 encourage sustainable practices. A planned carbon tax by 2026 aims to accelerate the transition to a circular economy. PETRONAS actively pursues circular economy initiatives, converting waste into products and implementing a closed-loop carbon management system.
Despite these efforts, significant environmental performance gaps persist. Malaysia’s high ranking as a global emitter (28th in 2022) and substantial carbon lock-in from fossil fuel projects highlight a disparity between commitments and actual performance.
Social & Governance: Strong Frameworks, Human Rights Test
| Building Social and Governance Practices Amid Persistent Challenges
The Malaysian O&G sector demonstrates a robust commitment to social and governance factors, particularly in health and safety, human rights, business ethics, and board diversity, though areas for improvement persist. Given the inherent risks of O&G operations, ensuring employee health and safety is paramount for regulatory compliance, reputation management, and cost control. Malaysian legislation, including the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA), Factories and Machinery Act (FMA), and Petroleum Safety Measures Act (PSMA), provides a comprehensive framework. Companies like PETRONAS have invested significantly in digitalising health, safety, and environment (HSE) incident management systems, upgrading crisis management tools, and enhancing emergency response capabilities through partnerships and training. Leading players like PETRONAS, Dialog, and Hengyuan Refining generally exhibit strong safety records, with Dialog and Hengyuan recording zero fatalities between 2020 and 2023. However, PETRONAS recorded two fatalities in 2023 , and faced a MYR 50,000 fine in 2022 for unsafe work conditions leading to a subcontractor’s death.
In human rights, O&G operations directly impact communities and workers, necessitating adherence to international principles like the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights. PETRONAS’s Human Rights Policy, effective April 2024, aims to strengthen its commitment to a safe working environment and human rights respect, with no reported violations of indigenous rights or discrimination in 2022. Nevertheless, the company has faced criticism for alleged environmental mismanagement and complicity in war crimes in South Sudan, accused of abandoning responsibilities upon its exit.
Driving ESG Forward: Key Strategic Pathways
| Investments to Accelerate Decarbonisation and Green Transition
To further enhance Malaysia’s O&G sector’s ESG outlook, a concerted effort across several strategic areas is imperative. The scorecard indicates that while social and governance aspects show progress, environmental challenges demand focused attention. A primary strategy involves continued development and investment in emission reduction technologies. Carbon capture, utilisation, and storage (CCUS) technologies are expected to attract over USD 10 billion in capital expenditure by 2030, supporting Malaysia’s National Energy Transition Roadmap (NETR) goal of capturing 40-80 million tonnes of CO2.
PETRONAS’s Kasawari Gas project exemplifies this, poised to be one of the largest offshore CCUS initiatives globally. The sector is also embracing green hydrogen, with PETRONAS partnering to develop Southeast Asia’s first commercial hydrogen electrolyser , and expanding solar energy adoption, as seen in Shell Malaysia’s rooftop solar installations and PETRONAS’s projects aimed at significant emission reductions.
Investment Flows Accelerate Green Energy Transition
| ESG Commitments Fueling Domestic and Foreign Investments
Malaysia’s O&G sector is experiencing a significant surge in both foreign and domestic investor interest, particularly in its clean energy transition, driven by enhanced ESG performance and governmental support through schemes like the 2018 Green SRI Sukuk Grant and the 2021 SRI Sukuk and Bond Grant Scheme.
Sarawak, a Malaysian state, is actively pursuing green hydrogen hub status, leveraging its hydropower potential and fostering international collaborations. The H2ornbill Project, a Sarawak-Japan collaboration involving Sumitomo and ENEOS, aims to produce clean hydrogen for local use and export to Japan. Similarly, the H2biscus Project, a Sarawak-South Korea collaboration with POSCO, Samsung E&A, and Lotte Chemical, targets substantial green hydrogen production for domestic needs and export to South Korea in the form of green ammonia and methanol.
Learn more about the information you can find in Speeda, the business intelligence data platform for Asia-focused research here.
Read the full report
Download our latest report with more insights for Malaysia’s oil and gas sector.
Thank you for your submission!
We will send an email with the download link to access the report shortly.
Follow our Linkedin Page !
Our latest updates on
ASEAN reports and webinars are posted here.



















